Which is Better for Brain Imaging: MRI vs CT Scan
When it comes to brain imaging, two popular imaging methods are widely used: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans. Both techniques provide valuable insights into brain health, but they differ in terms of their technology and diagnostic capabilities.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between MRI and CT scans, helping you understand which one is better for brain imaging and detecting brain tumors.
What Is an MRI?
MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body's internal structures. In the case of brain imaging, MRI provides highly accurate and detailed images of the human brain, allowing healthcare professionals to assess its anatomy and detect any abnormalities.
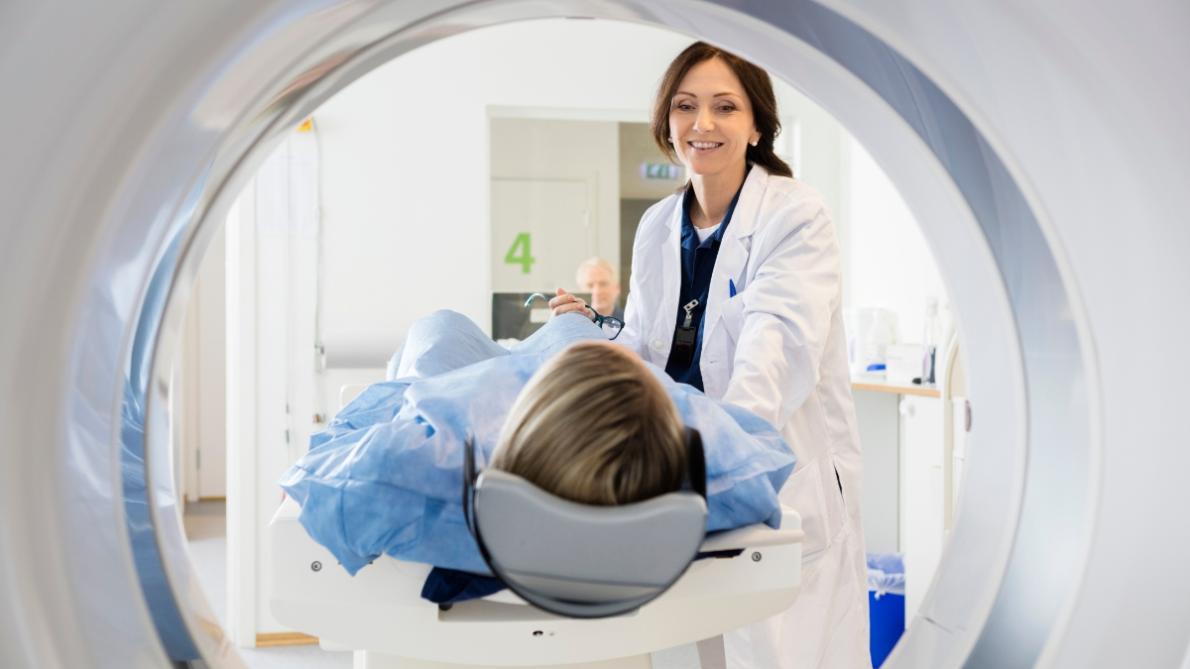
Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for repeated imaging. During an MRI scan, the patient lies on a movable table that slides into a cylindrical machine. It is important to remain still during the procedure to ensure clear images.
What Is a CT Scan?
A CT scan, or Computed Tomography scan, is another medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body. It is particularly useful for examining bone structures and detecting acute conditions such as brain hemorrhages, fractures, and tumors with calcifications.
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves through a doughnut-shaped machine, which emits X-ray beams from various angles. The images obtained are then reconstructed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images of the brain.
CT scans are relatively quick compared to MRI scans, making them useful in emergency situations where immediate diagnosis is crucial. However, it is important to note that CT scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which carries a potential risk, especially with frequent or unnecessary scans.
MRI Vs CT Scan: Comparison
Technology
- MRI: Utilizes powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of brain structures and tissues.
- CT Scan: Relies on X-rays to produce cross-sectional images of the brain.
Image Quality
- MRI: Offers superior image quality with exceptional detail, allowing for better visualization of soft tissues, blood vessels, and abnormalities.
- CT Scan: Provides good image quality, but not as detailed as MRI scans. It is particularly effective at highlighting bone structures.
Safety
- MRI: Generally considered safe, as it does not expose patients to ionizing radiation. However, certain individuals with metallic implants or claustrophobia may face limitations.
- CT Scan: Involves exposure to ionizing radiation, which may pose a risk, especially with frequent or unnecessary scans.
Diagnostic Capabilities
- MRI: Highly effective for detecting brain tumors, vascular disorders, multiple sclerosis, and neurological conditions. It provides exceptional clarity and helps differentiate between healthy and diseased tissues.
- CT Scan: Ideal for detecting acute conditions like brain hemorrhages, fractures, and tumors with calcifications. It is faster than MRI and often used in emergency situations.
MRI Vs CT Scan: Which Is Better for Brain Imaging?
MRI scans are better for brain imaging as they are the most sensitive brain imaging technique currently available, especially for the brain. Because of this, it is a better option for detecting brain tumors.
Advantages of CT Scan: Brain Imaging
- Speed: Significantly faster than MRI, making them the preferred choice in cases of trauma and other acute neurological emergencies.
- Cost: More cost-effective compared to MRI, and they can effectively rule out many neurological disorders.
- Motion Tolerance: This neuroimaging technique is less sensitive to patient motion during the examination due to its faster imaging process.
- Patient Comfort: CT scans may be more suitable for claustrophobic or heavily built patients, as they do not require the patient to enter a confined space like an MRI machine.
- Bone Evaluation: Provide a detailed evaluation of cortical bone, making them valuable for assessing bone structures and potential fractures.
- Detection Capabilities: Offer accurate detection of calcifications and metal foreign bodies within the brain.
- Compatibility with Medical Devices: Can be safely performed on patients with implantable medical devices, such as cardiac pacemakers, ferromagnetic vascular clips, and nerve stimulators.
Advantages of MRI Scan: Brain Imaging
- Safety: MRI scans do not involve the use of ionizing radiation, making them a preferred choice over CT scans, especially for children and patients requiring multiple imaging examinations.
- Superior Soft Tissue Contrast: Offers a wider range of available soft tissue contrast, enabling greater detail in depicting brain anatomy. It is highly sensitive and specific in identifying abnormalities within the brain itself.
- Multi-Plane Imaging: MRI scanning allows imaging in any desired plane without physically moving the patient, providing flexibility and comprehensive visualization of brain structures.
- Lower Risk of Allergic Reactions: MRI contrast agents have a significantly smaller risk of causing potentially life-threatening allergic reactions compared to other imaging modalities.
- Artifact-Free Evaluation: Allows the evaluation of structures that may be obscured by artifacts from the bone in CT images. This enhances the accuracy and clarity of the diagnostic information obtained.
MRI & CT Scans: What You Need To Know
Are MRI and CT scans painful?
Neither procedure is painful. However, some patients may experience discomfort due to the confined space in MRI machines.
Which scan is more expensive?
Generally, MRI scans tend to be more expensive compared to CT scans due to the advanced technology involved.
How long does each scan take?
CT scans are quicker and usually take only a few minutes, while MRI scans can take between 15 minutes to an hour, depending on the type and purpose of the scan.
Can a CT scan detect cancer?
CT scans can detect certain types of cancer such as bladder cancer, kidney cancer, ovarian cancer, stomach cancer, and even colon cancer.
Best Brain Cancer Clinic
When it comes to brain cancer treatment, the Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center at Duke stands out as one of the best brain cancer clinics. Our team of dedicated doctors is at the forefront of research and is committed to providing exceptional care to our patients. We strive to instill hope and empower individuals facing a brain tumor diagnosis.
Discover why the Preston Robert Tisch Brain Tumor Center is renowned for its expertise in brain tumor treatment. Schedule an appointment today and take a step towards effective treatment and a brighter future.